For Physicians
VTD HEADACHE ASSESSMENT REPORT
The patient can consult a physician with the received assessment report, or
a physician can search for the report on
this website using the report number. This assessment report will be shown in the form of “ VTD
HEADACHE ASSESSMENT REPORT ”. The physician can use this report as a tool for additional
assessment. This report will be divided into 6 parts as
follows (see the form below) :
- Primary report will provide the suggestions for the patient.
- Patient’s history will be filled in the report. The suspected red flags [ref. 1] will be highlighted with red color.
- Features of some important primary headaches are presented for clinical correlation.
- Diagnostic criteria of these primary headaches are listed as the “Diagnostic
Criteria Tracer” (see Description in the form), which serves as a diagnostic
guide. These criteria are based on ICHD-3 [ref. 2].
If the patient’s history resembles the characteristic patterns of any primary headaches, these primary headache types will be marked to suggest the likely headache type, but without indicating a diagnosis. Once the patient’s clinical features fulfill the diagnostic criteria, without evidence suggesting secondary headache, the marked primary headache type may then be diagnosed.
- Description [ref. 2] is provided on page 2.
- Groups of Headache Disorder [ref. 2] are presented on page 2 for differential diagnosis.
FORM of VTD HEADACHE ASSESSMENT REPORT
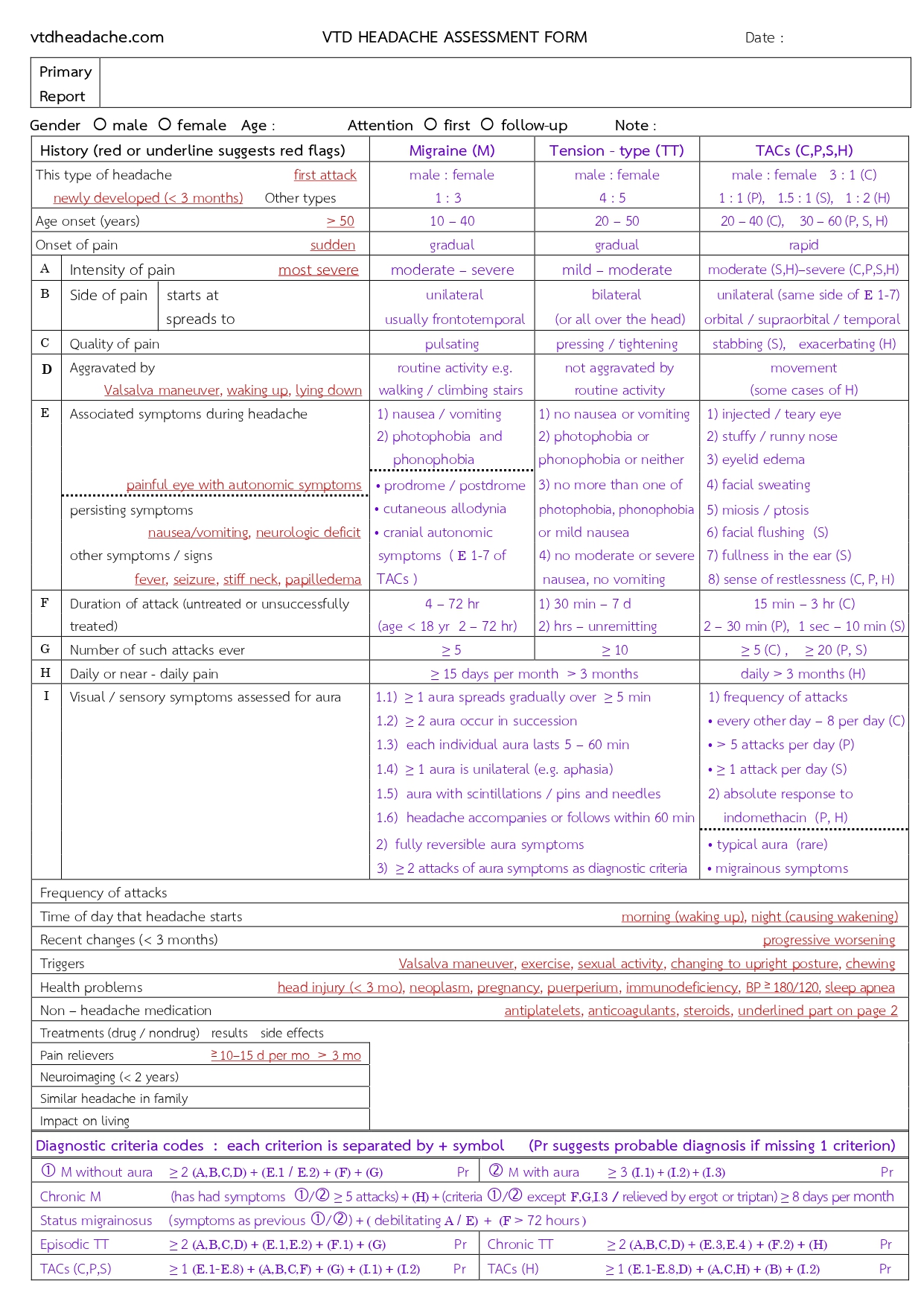

Manage The Form
( All red flags are shown in this form )


Physicians can use this form for assessment without using the questionnaire.
Manage The Form
RED FLAGS
Red flags are specific history, symptoms, or signs that are often associated with secondary
headaches. However, they may
also occur in primary headaches. Importantly, red flags may suggest underlying causative
disorders and heighten
awareness of secondary headaches. A combination of compatible red flags may increase their
significance.
The red flags used in the VTD HEADACHE ASSESSMENT are listed below, along with their
suggested possible disorders
(SNNOOP10) [ref.1,2].
Systemic symptoms including fever
• Fever : infections
Neoplasm in history
• Neoplasm (health problem) :
neoplasms, metastasis
Neurologic deficit or dysfunction including decreased consciousness
• Neurologic deficit • Seizure : vascular
or
nonvascular disorders, infections
Onset of headache is sudden or abrupt
• Sudden and severe : subarachnoid
hemorrhage,
vascular disorders
Older age (after 50 years)
• Age onset (years) > 50
: neoplasms, vascular or nonvascular disorders, giant cell
arteritis
Pattern Change or recent onset of new headache
• First attack • Newly developed (< 3 months)
: neoplasms, vascular or nonvascular disorders
Positional headache
• Changing to upright posture
: intracranial hypotension
Precipitated by sneezing, coughing, or exercise
• Valsalva
: posterior fossa lesions, Chiari malformation
• Exercise or sexual activity (on first occurrence)
: subarachnoid hemorrhage, vascular disorders
• Chewing
: giant cell arteritis, TMJ disorders
Papilledema
• papilledema
: neoplasms, nonvascular disorders, intracranial hypertension
Progressive headache and atypical presentations
• Progressive worsening
: neoplasms, nonvascular disorders
Pregnancy or puerperium
• Pregnancy or puerperium
: hypertension, preeclampsia, eclampsia, cerebral sinus thrombosis,
hypothyroidism, postdural puncture
Painful eye with autonomic features
• Painful eye with autonomic symptoms
: pathology in posterior fossa, pituitary region, or cavernous sinus; Tolosa-Hunt syndrome;
ophthalmic causes
Posttraumatic onset of headache
• Head injury (< 3 months)
: posttraumatic headache, subdural hematoma
Pathology of the immune system such as HIV
• Immunodeficiency • steroids
: opportunistic infections
Painkiller overuse or new drug at onset of headache
• Pain relievers > 10-15 days/month > 3 months
: medication-overuse headache
• Using the drugs underlined on page 2 of the form
: drug-induced headache
• Antiplatelets, anticoagulants
: intracranial hemorrhage
References
1) Thien Phu Do, et al. Red and orange flags for secondary headaches in clinical practice :
SNNOOP10 list. Neurology 2019 ; 92 : 134 - 144. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6340385
2) Headache Classification Committee of The International Headache Society (IHS). The
International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (ICHD-3). Cephalalgia 2018 ; 38
: 1 - 211. https://ichd-3.org
